A Guide to Blogging and CMS
What does blogging do?
Content management systems (CMS) and blogs are excellent web-based platforms to host and maintain records of creative content and stories. Your blogging platform can host text, images and embedded videos, and provide a landing page that can be linked to various sources of traditional and social media channels/platforms.
Further, tagging blog posts enables segmentation of content by themes—allowing you and your audiences to quickly sift through content. to post on various social or curation platforms. Nonprofits and international development NGOs are moving towards blogs that no longer comprise just text and images. Many organizations are beginning to integrate multi-media curation platforms and other sources of technology to create three-dimensional stories.
Further, blogs are focusing on the stories of single individuals, rather than large segments of the population. As the number of media sources rise, having high-quality content that attracts and motivates your audiences will be key in maintaining a successful blog that promotes action.
There are multiple platforms available for blogging, including WordPress, Joomla, Django and Drupal, among others. These platforms are versatile and allow you to create blogs that can expand reach and resources by connecting with audiences emotionally.
What do I need to use a blogging platform?
- Technology: Computer/smartphone/tablet, Internet connection
- Suggested Frequency: Depends on your capacity to create original content
What can I share on a blog?
You can publish and share posts that include text, photos, quotes, links, music and videos. Your blog posts can be as long or as short as you like, but typically they are between 200 and 750 words.
How do I use a CMS/blog?
From a content management and publishing standpoint, there are a several different popular blogging platforms that you can use to easily create and update a blog. Online guides for WordPress, Joomla, Django, and Drupal, are among the best places to start exploring functionality questions.
What are the strengths and limitations of WordPress?
Recommended use: Perfect for visually appealing, easy-to-manage blogs with or without multiple authors/users.
Pros
- Scalable. WordPress offers options ranging from smaller blogs for start-ups to complex platforms that support the websites of major organizations.
- Affordable. A broad range of turnkey templates and plugins are available for little to no cost.
- Intuitive. An intuitive user interface allows post authors in your organization to learn the system quickly.
- Collaborative. It is easy to edit blog posts with multiple logins and is very conducive to workflow management.
- Customizable. The look and feel of your blog can be 100 percent customized to your brand.
- Extensive plugins. Plugins allow you to extend the functionality of your WordPress site without knowing any computer programming. There are over 10,000 plugins available that help you add a variety of functionality to your blog, such as social media sharing, search engine optimization, photo slideshows and much more.
- Support. WordPress is supported by a thriving community. There are thousands of designers, developers and enthusiasts to help you troubleshoot, along with a knowledgeable support staff. Search engine optimization. The construction of WordPress blog code is consistent and streamlined without excessive HTML code, which Google prefers for indexing.
Cons
- Cost logistics.
- Payment models may vary.
- Website requirements. Current website infrastructure must meet specific requirements—and integrating WordPress may require customization depending on your existing website. View WordPress requirements.
- Constant updates. WordPress requires frequent maintenance and updating, which may require changes to your template or plugins. With every update, you risk issues with your website template—which can cost additional money.
- Security. WordPress is often targeted by hackers and can be vulnerable to security issues.
What are the strengths and limitations of Django?
Pros
- Free. Django is free and open source.
- Customizable. Your organization can customize user interface and build your blog from the ground up.
- Accessible resources. Free APIs and documentation tutorials are available.
- Integrated. Django is used by leading tech brands, including Instagram and Pinterest.
Cons
- Knowledge barrier. Blog post authors in your organization should have a solid foundational knowledge of Python/Web development.
What are the strengths and limitation of Joomla?
Recommended use: A stable, no-frills option for small to mid-size organizations
Pros
- Free. Joomla is free and an open source software.
- Customizable. The software allows for massive levels of customization and custom development.
- Established. The mature, well-documented open source project is one of the top choices as a blogging platform.
- Available tools. A large library of stable and powerful plugins and extensions is available.
- Sophisticated hierarchies. Recent versions of Joomla include a more complex navigation pattern that is able to support more than two-level hierarchies. This provides for more in-depth websites with hundreds of pages, a feature not available on WordPress.
Cons
- Knowledge barrier. The setup and learning curve can be daunting.
- Too Technical. Joomla is more complex than WordPress and other more simple platforms, so you may require some background in websites and design principles.
- Lesser search engine optimization capability. WordPress tends to be more compatible with search engine optimization than Joomla.
- Not intuitive. Joomla is not as intuitive and user-friendly as WordPress.
What are the strengths and limitations of Drupal?
Recommended use: Ideal for large projects in which stability, scalability and power are more important than aesthetics and customizations.
Pros
- Free. Drupal is free and an open source software.
- Scalable. The software is highly scalable and can meet a variety of needs.
- Customizable. The software allows for massive levels of customization and even custom development, on par with Joomla.
- Available tools. A large library of stable and powerful plugins and extensions is available.
- Community support. An extensive community and commercial services vendors are available to support and extend systems.
- Variety of content types. Drupal is known for creating and managing many content types, including videos, polls, user management, text, blogs and podcasts.
- Scalable. The software is highly scalable and can meet a variety of needs.
- Customizable. The software allows for massive levels of customization and even custom development, on par with Joomla.
- Available tools. A large library of stable and powerful plugins and extensions is available.
- Community support. An extensive community and commercial services vendors are available to support and extend systems.
- Variety of content types. Drupal is known for creating and managing many content types, including videos, polls, user management, text, blogs, podcasts, statistics and others.
Cons
- Installation and modification. The script is not very user-friendly and requires advanced knowledge to install and modify. WordPress and Joomla are simpler to use, but offer fewer functionalities.
- Long loading times. The large breadth of tools in Drupal makes blogs slow to load.
- Lacks quality free plugins. While many quality plugins are available, very few of them are free.
- Knowledge barrier. The setup and learning curve can be daunting.
- Too customizable. With a multitude of options and design concepts available, it is easy to create blogs that are difficult to navigate and aesthetically displeasing.
Why should I have a blog?
Content management systems and blogs are excellent platforms to host and maintain records of creative content and stories. Your blog can host text, images, and embedded videos, and provide a landing page that can be linked to various sources of traditional and social media platforms. Blogs are also an efficient means of search engine optimization.
What story formats work best on a blog?
Blogs tend to be heavy in text and are accompanied by complementary images, videos and other multimedia. You can also create a video or photo blog if you have the capacity to regularly produce those types of content.
What’s the most effective way to share stories on a blog?
Plan ahead and create a detailed editorial calendar for producing original content. Most blogging platforms have built-in capabilities to schedule and publish posts according to your organization’s editorial calendar.
How do blog users share and engage with content?
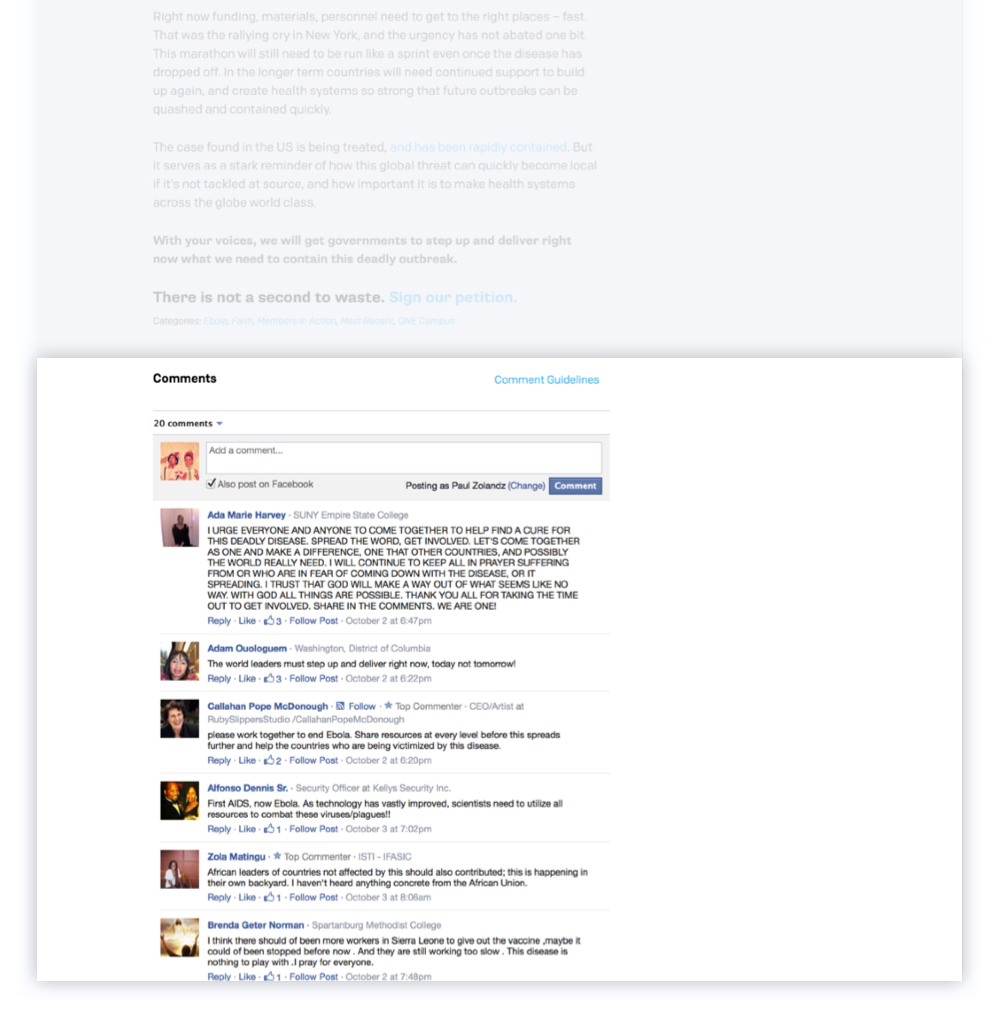
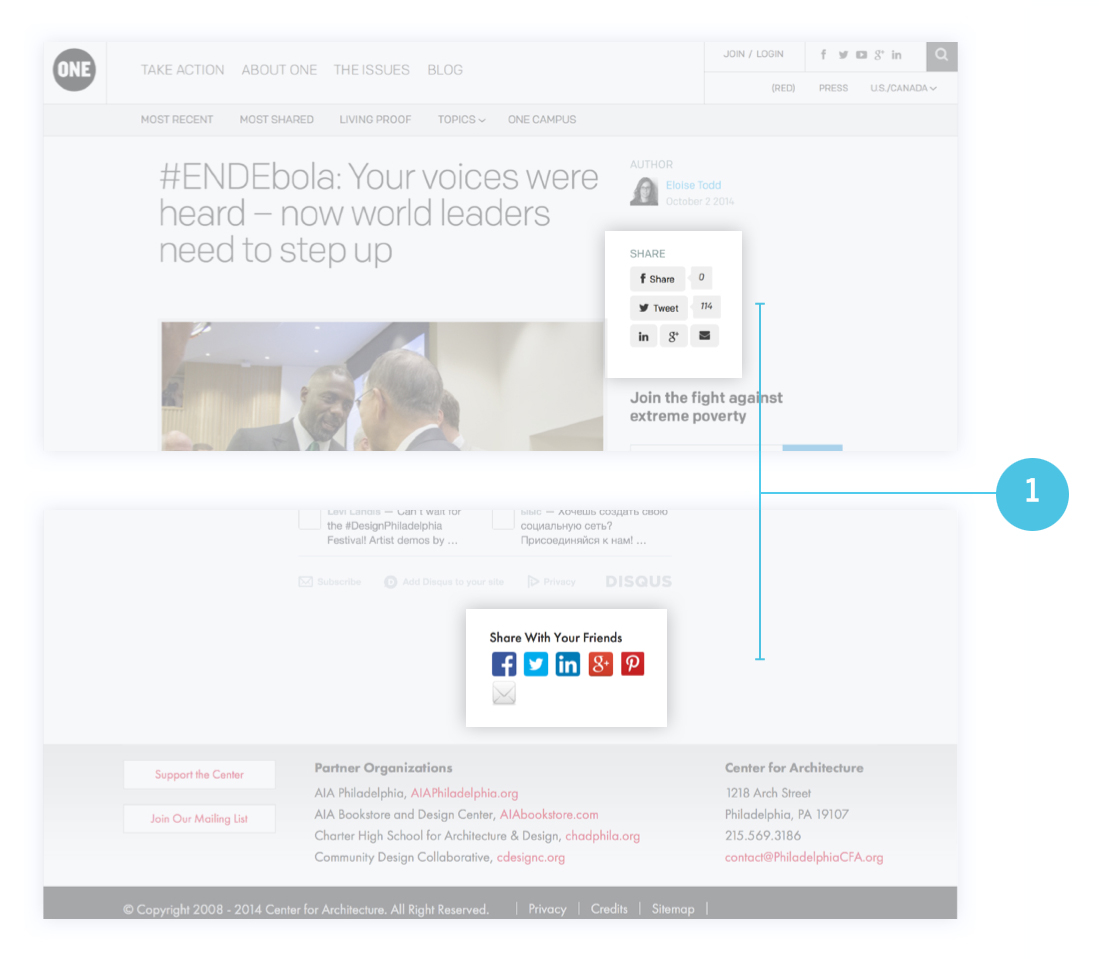
- Share. Readers may share your blog posts on their social media networks and through email.
- Subscribe. Readers may subscribe to your blog if they find your content engaging. This will give them constant updates on your new content.
How should I engage users on a blog?
- Social media. Make sure to share your blog posts on your social media channels to make it visible to your target audience.
- Email. Send an update to your email lists about your articles. You can also consider including your blog content—or a preview of posts that link to the full post—in your email newsletter.
- Respond. Try to respond to comments from your readers whenever possible to increase interaction and spark discussions.
- Be consistent. Regularly posting articles will help build a loyal following for your blog.
- Calls to action. Use your blog to deepen your relationship with your audience. Ask them do specific tasks like joining your email list, attending an event or signing up for volunteering. Also, consider asking them to share a story in the comments sections. This is your opportunity to get them involved in your cause.
- Headlines. Invest time to write headlines that are shareable and Tweet-worthy.
How can I increase visibility for my blog?
- Be active and consistent. Aim to produce a steady stream of quality content to keep your audience interested.
- Share. Remember to share your blog posts through your website, social media, email and newsletter.
- Search engine optimization. Invest time in a search engine optimization strategy for your blog. This will help your content reach people who are interested in your organization and issue areas.
- Feature thought leaders. Invite experts in your field or issue area to contribute as guest bloggers.
- Timely stories. Talk about stories that tie to current events. You can also do real time reporting from a conference, field visit or legislative session.
- Cross-promote. Cross-promote and reuse all the content you create for your website, print magazines and newsletter.
RELATED ON STORYTELLING FOR GOOD
EXTERNAL RESOURCES
Related, on Storytelling for Good
A Guide to Tumblr
- 3 Saved
Rhythm: The Most Important Thing About Your Organization That You Don’t Understand
- 3 Saved
Project Renewal Raises $80,000 With CauseVox and #GivingTuesday
Evaluating Storytelling: Where to Start?
- 1 Saved
A Guide to YouTube
- 1 Saved
Mamas Day: Recognizing a Profound Act of Community
- 1 Comment






2 Comments
our vision is to sustain democracy in Africa,fight corruption,enhance entrepreneurship development programme to ensure job opportunities in Africa,particularly Nigeria.
Go ahead